Great Nicobar International Airport and India’s Ocean Strategy
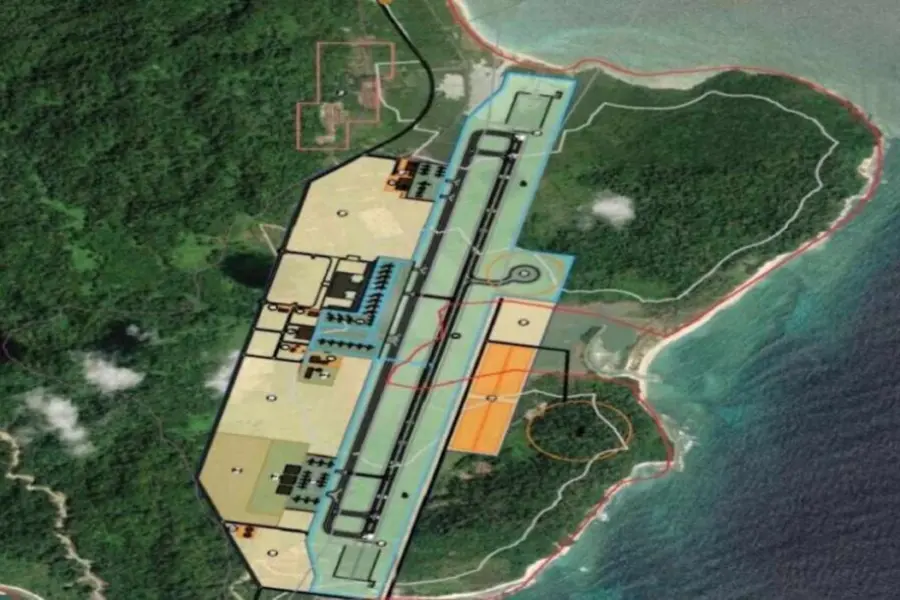
Under the direction of Narendra Modi, the government has commenced work on The Great Nicobar International Airport. It is one of India’s most valuable infrastructure projects strategically located at the southernmost region of India. The airport serves as a dual facility to support National Security. While providing a new opportunity for connectivity and Economic Development in Asia and The Indian Ocean Region.
Exclusive documents that indicate the airport will also strengthen India’s Defense Response Capabilities. This will reduce the Response Time for Military Operations in the Eastern Indian Ocean Region. Recent news has illustrated that the Government’s Long Term Strategic Investment Priority is in strategically critical geopolitical areas.
Strategic Military and Tactical Position
The proposed airport will be located on Great Nicobar Island. It is an area within the Six Degree Channel, one of the most heavily trafficked Maritime Trade Routes in the World. This geographical position provides a significant Operational Advantage for India. Given that the nearest Major Commercial Airport is over 500 Kilometres away in Port Blair.
Upon becoming operational, the airport will allow for larger Military Aircraft to operate closer to Essential Sea Routes. Thereby increasing India’s ability to monitor and respond throughout the Eastern Indian Ocean.
Based on existing MTC documents, it has been forecasted that military air traffic will be incorporated into the plans for the airport by the early 2030s. This highlights the military aviation use for the airport over the long term.
This airport will have both types of aviation used by both civil aviation and military aviation.
The Indian Navy is responsible for performing the air traffic control and Air Traffic Services for Military and civilian operations. While providing surface areas, facilities, and services that support civil aviation.
Before the new airport commences operation, agreements will need to be made that delineate the parameters. Guidelines for including civilian passengers at Naval Air Stations used jointly. The Guidelines include the establishment and use of terminals used for commercial passenger service.
Hurdles in the Geography and Environment
Great Nicobar Island is sparsely populated and is mainly covered by densely forested area. It is surrounded on three sides by mountains. To satisfy air safety regulations, the proposed plan calls for necessary cutting of the hills (to satisfy OLS requirements). The materials removed during the excavating process will be reused at the new airport project location. Also, among other infrastructure uses on Great Nicobar island.
Flight routes have been planned to fly over ocean areas and not across populated areas. It resulted in fewer low-level flights through populated regions. Thereby reducing safety issues related to low-level flying. Environmental impacts are also being reduced.
Improvement of Accessibility and Economic Activity for Travel
Along with providing security-related benefits, the construction of the airport will help overcome decades of isolation faced by Great Nicobar Island and its surrounding islands. The proximity of Great Nicobar to popular tourist destinations, such as Phuket and Langkawi (within 500 km), represents a distinct advantage compared to being located over 1,500 km from mainland India.
The strategic location of Great Nicobar will allow for developing luxury tourism and access to international travel networks, creating economic opportunities and sustainable jobs for locals.
Economic growth & sustainability
The new airport is a greenfield site; the projected traffic growth is based on the anticipated development of the urban and economic environment instead of historical traffic data. Based on population forecasts, Great Nicobar will have a projected population in 2040 of around 325,000. The new airport is anticipated to have a passenger handling capacity of around 1,350,000 passengers annually.
The new airport will be built over a 50-year period (2025 to 2075) and will be developed in conjunction with the projected use of the airport to increase capacity incrementally as necessary. In addition to being built to GRIHA-5 (Green Rating for Integrated Habitat Assessment) standards for sustainable development, the airport terminal will also be built to be carbon-neutral. Therefore, renewable energy, advanced drainage systems and innovative engineering are central to the development.
A Strategic Gateway for India’s Southern Frontier
The Great Nicobar International Airport is envisioned not just as an aviation facility, but as a strategic gateway that reinforces India’s maritime security, drives economic opportunity, and connects the country’s southernmost frontier to the rest of India and the world — a key highlight in ongoing recent news updates on India’s infrastructure and defence strategy.






Квартиры на сутки
Снять квартиру на сутки удобно для семьи или пары.
– Можно готовить дома.
– Свободное пространство и несколько комнат.
– Удобно для деловых поездок и отпуска.
сервис бронирования жилья посуточно
@airbn@b77 https://sutochny.ru/poleznyye-sovety/
Kebetbetlogin, solid login process, and a fair welcome bonus caught my eye. The betting odds are competitive, too, which is key. You should check this out: kebetbetlogin
Decided to try my luck at jljl333casino and surprisingly had some fun. The website looked good and was easy to use, big plus from me. Check it out before you disagree! jljl333casino
Downloaded the 222winapp and it’s actually pretty decent! Runs smoothly on my phone, and I can get my game on wherever I am. Thumbs up for convenience! 222winapp
Yo, ok365app is pretty slick! Downloaded it last week and already hooked. Easy to use and the games are actually fun. Check it out ok365app
Pinasgems? Now that sounds interesting! Checking it out now… Seems promising! If you’re looking for something new, might be worth digging around here. Explore the gems: pinasgems
3333winbet, pretty easy to get started. They got a good selection of games. Had a few losses but also managed to snag some wins. Give it go. 3333winbet
R7betbr is becoming my favorite platform because of its promotions and great odds, everything is on point in this cool platform and they are up to date with the games and promos, check the latest promotions in their website: r7betbr
Baccarat patterns are fascinating – so much relies on recognizing subtle shifts! Seeing platforms like jjj777 use data to personalize the experience-even with bonuses-is a smart move for players. It’s about informed decisions, right?
That’s a solid point about bankroll management – crucial for any table game! Seeing platforms like jl56 slot download offer quick, secure deposits (even via GCash!) definitely helps stay in the action longer. Good article!
Hey, been looking for a solid portal to B52? B52dangnhap.com seems like a decent option. Easy to get in, no fuss. Try it out if you need a quick link, here’s b52dangnhap!
Bet188link, đường dẫn mới của 188bet hả? Mấy cái link này hay bị chặn lắm, phải có cái dự phòng thế này mới yên tâm được. Thanks for sharing bet188link.
I have been absent for some time, but now I remember why I used to love this website. Thanks , I will try and check back more often. How frequently you update your website?
Alright, vn88me, sounds trustworthy. And that’s what I need to win. Let’s see if vn88me I gonna be able to party!
Looking for some Jili action? Jili77download’s got you covered. Simple, quick download. Time to chase those jackpots! jili77download
SV388 10naga, huh? Never tried that before. Live cockfighting isn’t my cup of tea but some folks dig it. Hope the odds are good whoever’s placing bets. sv388 10naga
Great post, I conceive people should larn a lot from this weblog its real user pleasant.
I’m not positive the place you are getting your information, but good topic. I needs to spend a while learning much more or working out more. Thank you for great info I was looking for this info for my mission.
Aw, this was a very nice post. In idea I want to put in writing like this moreover – taking time and actual effort to make an excellent article… however what can I say… I procrastinate alot and not at all appear to get one thing done.
Absolutely composed subject material, Really enjoyed studying.
I really like your writing style, fantastic info , thanks for putting up :D.
You made some decent points there. I looked on the internet for the issue and found most persons will consent with your blog.
Hello my loved one! I want to say that this article is awesome, nice written and include approximately all significant infos. I would like to see more posts like this .
I think this site has got some really wonderful info for everyone. “He is able who thinks he is able.” by Buddha.
Regards for this wondrous post, I am glad I noticed this internet site on yahoo.
I am constantly searching online for articles that can benefit me. Thanks!
What i don’t understood is actually how you are not really much more well-liked than you might be now. You are so intelligent. You realize thus considerably relating to this subject, made me personally consider it from so many varied angles. Its like women and men aren’t fascinated unless it is one thing to accomplish with Lady gaga! Your own stuffs outstanding. Always maintain it up!
I’m now not positive where you are getting your information, however great topic. I must spend some time finding out more or working out more. Thanks for wonderful info I used to be searching for this information for my mission.